This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
General Protein Information
FOXP2 is a member of a subfamily (FOXP) of the forkhead box transcription factors. The FOXP2 homolog in Drosophila melanogaster is known as fkh and in Caenorhabditis elegans as fkh-7. There are no known homologs of FOXP2 in Arabidopsis. FOXP2 is known as FOXP2 in zebra finch, chimpanzee, house mouse, wooly-horseshoe bat, and zebra fish. Forkhead box P proteins are classified by the presence of several domains, such as glutamine-rich regions, a zinc finger, a leucine zipper and a forkhead DNA binding domain. The leucine zippers of two monomer proteins interact to promote dimerization of FOXP2 and the assembly of protein/DNA complex. The forkhead domain, also known as a winged-helix domain, mediates the DNA recognition required for proper regulation of target genes (1). Furthermore, it is this domain where disease-causing mutations occur, resulting in several disorders, including speech and language disorders.
Using ExPASy-PeptideMass, FOXP2, with an amino acid sequence of 715 residues, was determined to have an average molecular weight of 78900.04 Da, and a theoretical isoelectric point of 6.09.
Using a hybrid prediction approach based on sequence composition, physico-chemical properties, dipeptide composition, and psi-BLAST, at ESLpred, FOXP2 is predicted to be localized to the nucleus (Other databases yielded concordant results). Such results are expected given the role of FOXP2 in regulation of gene expression.
Using ExPASy-FindMod and EBI-RESID, no post-translational modifications were identified in FOXP2. Although there are no known PTMs of FOXP2, it is likely that the protein is post-translationally modified, as the transcription factor has been shown to act as a repressor and an activator of mulitple genes in human neuron-like cells (2).
Protein Sequences
The sequences for the three isoforms of FOXP2 can be found at NCBI by following the links below.
Isoform I
Isoform II
Isoform III
Protein Domains
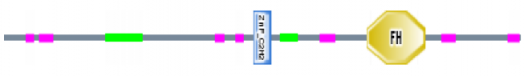
Above is a representation of domains within FOXP2 found using the SMART database. Pink segments represent regions of low complexity. Green segments represent coiled-coil regions. The N-terminal coiled-coil segment represents the glutamine-rich region spanning positions 140 to 192. The domain labled ZnF_C2H2 represents the zinc finger motif spanning positions 346 to 371. The domain labeled FH represents the forkhead DNA binding domain spanning positions 502 to 583. Although not depicted here, the leucine zipper domain spans the zinc finger domain, ending roughly 50 residues N-terminal of the forkhead domain (1). Other than the absence of the leucine-zipper domain, all other motif predictions are consistent with the literature on what is known about FOXP2.
Structure
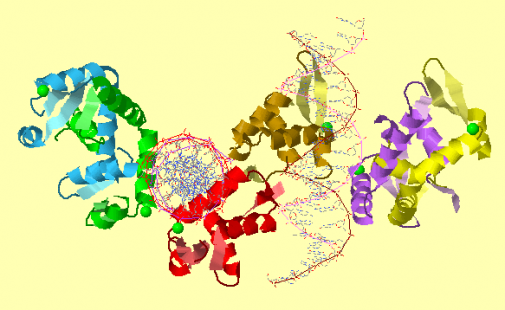
The Jmol image shown represents the structure of FOXP2 bound to DNA. The image contains six copies of FOXP2, with two copies in the monomeric form and four in the dimeric form. The golden and red structures represent the monomeric forms of FOXP2 bound to DNA. These forms bind directly to equivalent sites on the two segments of DNA. Furthermore, when bound to DNA, these forms fold into the winged-helix motif. The purple-yellow structure and the blue-green structure both represent dimeric forms of FOXP2. The dimeric forms of FOXP2 loosely associate with the DNA strands. (1) This image was obtained from EBI-PDBsum database.
References
1. Stroud JC, Wu Y, Bates DL, Han A, Nowick K, Paabo S, Tong H, and Chen L. (2006) Structure of the forkhead domain of FOXP2 bound to DNA. Structure 14:159-166. PMID: 16407075
2. Vernes SC, Spiteri E, Nicod J, Groszer M, Taylor JM, Davies KE, Geschwind DH, and Fisher SE. (2007) High-throughput analysis of promoter occupancy reveals direct neural targets of FOXP2, a gene mutated in speech and language disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 81:1232-1250. PMID: 17999362
Databases
EBI-PDBsum
EBI-RESID
ESLpred
ExPASy
SMART
Andrew Tritt
tritt at wisc dot edu
Last Updated: 05/13/2009
Genetics 677
