Gene Sequence....etc.
This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Molecular sequences
FOXP2, also known as SPCH1, CAGH44, TNRC10, and DKFZp686H1726, is found on chromosome 7 in humans and has three known isoforms (5). The sequences for these isoforms and their respective transcript variants can be found at NCBI via the following links:
Isoform I
Transcript variant 1
Isoform II
Transcript variant 2
Isoform III
Transcript variant 3
Further analysis of this gene will use mRNA complete coding sequences protein sequences. The human sequence for this can be found at: BC143866.1
Homologs
FOXP2 complete coding sequence for zebrafish, woolly horseshoe bat, zebra finch, chimpanzee and mouse can be found at the following links.
Danio rerio DQ061052.1
Rhinoluphus luctus EU076406.1
Taeniopygia guttata AY395709.1
Pan troglodytes AY143178.1
Mus musculus AF339106.1
Alignment
A protein sequence alignment of the FOXP2 homolog in woolly horseshoe bat, zebra finch, chimpanzee, mouse and human was conducted using T-COFFEE. When aligned, FOXP2 shows a similarity of 57, which is relatively high when considering the evolutionary distance between these organisms, suggesting that this protein likely has a highly conserved functional role.
The alignment can viewed by downloading the PDF below. Sequences used for alignment were obtained from NCBI. Follow above links for sequences.
| foxp2_aa_alignment.pdf | |
| File Size: | 52 kb |
| File Type: | |
An alignment of the human isoforms was also conducted using T-COFFEE. The three isoforms show a similarity of 80. Most of the variation within the isoforms exists at the N-terminus, with an insertion of 92 and 117 base pairs in Isoforms I and II, respectively. Outside of this region, the protein sequence is almost completely non-variable across the three isoforms.
The alignment can viewed by downloading the PDF below. Sequences used for alignment were obtained from NCBI. Follow above links for sequences.
| foxp2_isoform_alignment.pdf | |
| File Size: | 30 kb |
| File Type: | |
Phylogeny
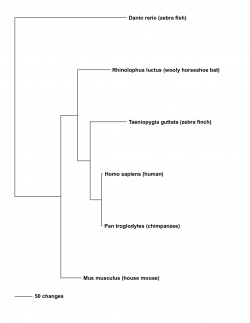
Given the connection between FOXP2 and unique phenotypes in song-birds, echolocating bats and mice, a phylogenetic tree construction was done to determine the phylogenetic relationships between FOXP2 homologs in these organisms. The shown tree was calculated under parsimony using PAUP* (3). Rhinolophus luctus was used to represent echolocating bats and Taeniopygia guttata was used to represent song-birds. Danio rerio (zebrafish) was used as the outgroup, and Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee) was used to increase the resolution of the relationships of the other organisms to humans, as chimpanzee is the most closely related living organism to humans.
As seen in the tree, the zebra finch is more closely related to the human than the woolly horseshoe bat and mouse are to the human. This evolutionary history is discordant with the known evolutionary relationship of these organisms (4), indicating that there is homoplasy among humans, echolocating bats and song-birds in the FOXP2 gene.
DNA Motifs
A DNA motif search on human complete coding sequence of FOXP2 was done using MOTIF. The query returned 105 motifs, many of which were motifs involved in DNA binding. This result would make sense given that FOXP2 is a known transcription factor. FOXP2 contains several GATA-binding factor domains, suggesting that FOXP2 is regulated by GATA-binding proteins. The gene also contains fork head domains, which is concordant with FOXP2 as a forkhead box transcription factor. FOXP2 also contains binding domains for many heat shock factors and stress-response elements, suggesting that FOXP2 may also play a role in stress response.
Protein Motifs
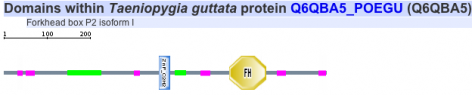
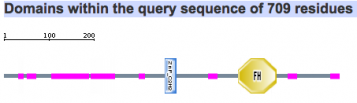
Protein motifs in human, mouse, chimpanzee, zebra finch, and woolly horseshoe bat were identified using SMART. All five homolgs contained two specific motifs for functional domains. The first motif of interest is a zinc finger domain, ZnF_C2H2, which is one of the most common DNA binding motifs in eukaryotes (1). The second motif is a forkhead domain, FH, also known as winged-helix in Drosophila. Forkhead domains, which bind DNA as monomers, are found in multiple transcription factor; however, the motif shows no similarity to any other DNA binding motifs. Such results are consistent with fact that FOXP2 is a transcription factor known to regulate many genes (2).
Human
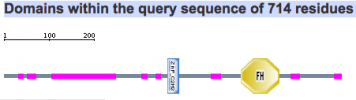
Mouse
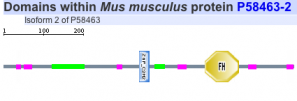
Zebra finch
Chimpanzee
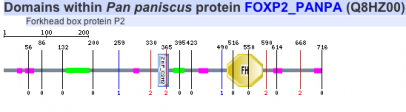
Woolly horseshoe bat
References
1. SMART (2009) FH domain annotation Retrieved February 28, 2009 from http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/do_annotation.pl?DOMAIN=FH&BLAST=DUMMY
2. SMART (2009) ZnF_C2H2 domain annotation Retrieved February 28, 2009 from http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/do_annotation.pl?DOMAIN=ZnF_C2H2&BLAST=DUMMY
3. Swofford, D.L. 2002. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts.
4. Tree of Life Web Project (1995-2004) Eutheria Retrieved on February 28, 2009 from http://tolweb.org/Eutheria/15997
5. NCBI (2009) Entrez Gene FOXP2 forkhead box P2 [Homo sapiens] Retrieved on February 28, 2009 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=93986&ordinal
pos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Gene.Gene_ResultsPanel.Gene_RVDocSum
Algorithm and sequence websites
TCOFFEE
NCBI
SMART
MOTIF
Andrew Tritt
tritt at wisc dot edu
Last Updated: 05/13/2009
Genetics 677
